On 31 Aug, 2015 With
Rembrandt, who is thought to have learned from Jacob van Swanenburgh and Pieter Lastmann, no doubt took stylistic cues from the Flemish Technique, the Venetian Technique, and the Direct Painting Technique. When observing his work, one can see that he experimented freely with them, moving between them, but he most certainly employed them all. Over time, as he learned each method, he incorporated aspects from all into a his style—while, of course, adding innovations of his own. Some of his paintings utilize wood as a canvas, as was common with the Flemish Technique, which he appears to have used predominantly in those works. In addition to this, a few of his small studies on wood panels seem to have utilized…
Read More
On 23 Aug, 2015 With
Oil painting techniques:Titian’s Palette Titian, the greatest Italian Renaissance painter of the Venetian school. He was recognized early in his own lifetime as a supremely great painter, and his reputation has in the intervening centuries never suffered a decline. Titian was one of the most versatile of Italian painters, equally adept with portraits, landscape backgrounds, and mythological and religious subjects. His painting methods, particularly in the application and use of color, would exercise a profound influence not only on painters of the Italian Renaissance, but on future generations of Western art. In 1590 the art theorist Giovanni Lomazzo declared him “the sun amidst small stars not only among the Italians but all the painters of the world.” During the course…
Read More
On 24 Jul, 2015 With
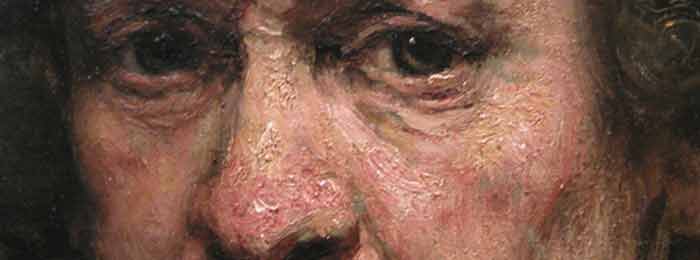
The Rembrandt Palette Rembrandt created his portraits with a small palette of colours dominated by dark earth tones and golden highlights. Remember the number of pigments available to the 17th century artist were miniscule when compared to those available to the modern artist. Rembrandt was unusual in that he used around hundred, but less than 20 pigments have been detected in Vermeer’s oeuvre. Portraits by Rembrandt have a special quality- the brilliant use of light to illumine faces, jewels and rich fabrics; the effective use of a limited palette, and the rich, dark, transparent backgrounds all set off the subjects of his portraiture in a way never seen before and often imitated afterwards. It has been said that a painter has…
Read More
On 21 Jul, 2015 With
Caravaggio’s painting technique: Using all of the technical and art historical information we now have on the paintings that can be firmly attributed to Caravaggio we can summarize his technical practices as follows: 1) Preference for using a linen canvas support mounted on a wooden strainer. 2) Preference for dark red-brown ground, often left visible, and used as mid-tones. 3) Use of dramatic, single-source lighting. 4) Use of incisions done free-hand in the still moist ground to establish the composition and fix the pose of his models. 5) Did not use preliminary sketches but began by loosely drawing the outline of forms in dark paint and locating major highlights in lead white (abozzo). 6) Used limited palette, primarily earth colors,…
Read More
On 18 Jul, 2015 With
Glazing Painting Techniques So, here I’ll give you way too much information on glazing (or indirect painting). But you can pick out what you need and forget the rest. It’ll be right here if you ever change your mind. Here’s the first rule (yes, in art rules are for breaking, but you have to understand the rule before you can break it most effectively) Fat Over Lean All mediums are fat, all opaque pigments without medium are lean. You want to paint opaquely first, with little or no medium. In subsequent layers you can move to using more medium because the oil will soak through to the first layer. Also, you don’t want the under layer to dry slower than…
Read More
On 18 Jul, 2015 With
Oil paintings techniques: Vermeer’s Palette Johannes Vermeer was a Dutch painter who specialized in domestic interior scenes of middle-class life. Vermeer was a moderately successful provincial genre painter in his lifetime. He seems never to have been particularly wealthy, leaving his wife and children in debt at his death, perhaps because he produced relatively few paintings. One aspect of his meticulous painting technique was Vermeer’s choice of pigments. He is best known for his frequent use of the very expensive ultramarine (The Milkmaid), and also lead-tin-yellow (A Lady Writing a Letter), madder lake (Christ in the House of Martha and Mary), and vermilion. He also painted with ochres, bone black and azurite. The claim that he utilized indian yellow in Woman Holding…
Read More
On 27 Jun, 2015 With
Palettes of Famous Artists. Zorn Palette Swedish painter Anders Zorn (1860-1920) has long been associated with a limited palette of four colors. Rosemary Hoffman, in the book Northern Light: Nordic Art at the Turn of the Century wrote, “Zorn was noted for executing paintings using a sober color scale limited to white, ochre, vermilion, and ivory black.” Hans Henrik Brummer, writing in the 1986 catalog on Zorn, said “basically his register was limited to black, white, earth yellows and vermilion; other pigments could be used if local accents were needed.” Several art teachers, such as Jeff Watts, use the “Zorn palette” (sometimes substituting cadmium red light for vermilion) as a teaching tool because it provides students with a finite range of color choices with a…
Read More
On 8 Jul, 2014 With
The underpainting was a core feature of the Venetian Method, and was often executed in opaque colour, rather than neutral greys. Many colour variations existed on this technique, such as Venetian Red and Flake White, with the only real limitation lying in the fact one ought limit one’s palette to lean paints (paints with a low rate of oil absorption) which are either opaque or very high in tinting strength. High tinting strength paints with a high oil absorption rate (fat paints) may be used only if mixed in minute quantities with very lean paints, so as to keep the underpainting leaner than the layers that will be applied above. Once the colour has dried, it can be modified with…
Read More
On 24 Jun, 2014 With
Titian and Giorgione were foremost among the pioneers of what we now call the Venetian Method of oil painting. The Venetian Method, or Venetian Technique, borrowed heavily from the Flemish Method, which saw the application of transparent glazes for the shadows, greater contrast between dark and light areas, and opaque highlights. The Venetian Method, however, deviates in some key areas, adding its own take on the Flemish process. While the glossy finish of the Flemish Method was ideal for small wood panels, on large paintings it was distracting and decidedly “overkill”; ergo, Titian refined the painting process to produce a less reflective surface. Most probably, he cut out sheen-enhancers like polymerized oils, balsams, and resins, and replaced them with…
Read More
On 10 Jun, 2014 With
Modern painting methods are far more rapid and direct than those used by the “old masters,” and as such, make replicating the works of these great artists a challenge, even when we render each colour and tone as closely as seems possible. The transparency and luminosity that was created by the heavily layered techniques of the old masters is found lacking regardless of one’s efforts to recreate colour and tone. This mysterious challenge invariably proves very frustrating when attempting to copy Renaissance art, with our current methods always producing something that appears heavy and overly opaque by contrast. Some have attributed the wondrous lustre and more translucent look of the old masters’ work to time, but that is not…
Read More