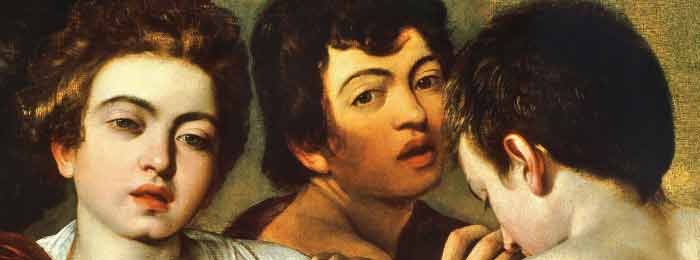On 24 Feb, 2017 With
A question from Farhad, Web Art Academy student
Hi Natalie,
I have been working on a painting for a few months now, as I only spend a few hours on weekends. It is actually my first painting done in multi layer technique. It is almost done except that I need to put some fine details on the fabric the man is wearing. It is a thick woolen fabric like the type used for men’s overcoat. What he is wearing has many folds which I have completed but need to know how to put these details.
There must be a way, technique to do that as I have seen ultra realistic paintings that show these detail, like wear and tear on a pair of jeans. I don’t want to go into that fine detail now but having some details on the folds adds more to the painting. Please let me know if you have any suggestion. …
Read More
On 31 Aug, 2015 With
Rembrandt, who is thought to have learned from Jacob van Swanenburgh and Pieter Lastmann, no doubt took stylistic cues from the Flemish Technique, the Venetian Technique, and the Direct Painting Technique. When observing his work, one can see that he experimented freely with them, moving between them, but he most certainly employed them all. Over time, as he learned each method, he incorporated aspects from all into a his style—while, of course, adding innovations of his own. Some of his paintings utilize wood as a canvas, as was common with the Flemish Technique, which he appears to have used predominantly in those works. In addition to this, a few of his small studies on wood panels seem to have utilized…
Read More
On 28 Aug, 2015 With
Renoir’s Palette Pierre-Auguste Renoir was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty, and especially feminine sensuality, it has been said that “Renoir is the final representative of a tradition which runs directly from Rubens to Watteau.” Renoir’s paintings are notable for their vibrant light and saturated color, most often focusing on people in intimate and candid compositions. The female nude was one of his primary subjects. In characteristic Impressionist style, Renoir suggested the details of a scene through freely brushed touches of color, so that his figures softly fuse with one another and their surroundings. One of the best known Impressionist works is Renoir’s 1876 Dance at Le…
Read More
On 18 Aug, 2015 With
Venetian Painting Techniques The painting techniques employed by Northern Renaissance artists strongly influenced the work of renowned painters, such as Titian and Giorgione, during the Italian Renaissance. Venetian artists also greatly impacted the styles of this period, notably the Van Eyck brothers. The oil painting techniques developed by these Flemish painters around the year 1400 combined the use of egg tempera and oil painting, with the underpainting being created using a grisaille technique of tempera, while pure colored oil glazes were carefully applied on top. This combination painting technique added remarkable lustre to their small panel paintings, resulting in striking jewel-tones, the most vivid hallmark of the brothers’ famous style. Prior to the Van Eyck brothers’ success with their combination…
Read More
On 9 Aug, 2015 With
Whistler’s Oil Painting Technique Whistler’s approach to portraiture in his late maturity was described by one of his sitters, Arthur J. Eddy, who posed for the artist in 1894: “He worked with great rapidity and long hours, but he used his colours thin and covered the canvas with innumerable coats of paint. The colours increased in depth and intensity as the work progressed. At first the entire figure was painted in greyish-brown tones, with very little flesh colour, the whole blending perfectly with the greyish-brown of the prepared canvas; then the entire background would be intensified a little; then the figure made a little stronger; then the background, and so on from day to day and week to week, and…
Read More
On 21 Jul, 2015 With
Caravaggio’s painting technique: Using all of the technical and art historical information we now have on the paintings that can be firmly attributed to Caravaggio we can summarize his technical practices as follows: 1) Preference for using a linen canvas support mounted on a wooden strainer. 2) Preference for dark red-brown ground, often left visible, and used as mid-tones. 3) Use of dramatic, single-source lighting. 4) Use of incisions done free-hand in the still moist ground to establish the composition and fix the pose of his models. 5) Did not use preliminary sketches but began by loosely drawing the outline of forms in dark paint and locating major highlights in lead white (abozzo). 6) Used limited palette, primarily earth colors,…
Read More
On 18 Jul, 2015 With
Glazing Painting Techniques So, here I’ll give you way too much information on glazing (or indirect painting). But you can pick out what you need and forget the rest. It’ll be right here if you ever change your mind. Here’s the first rule (yes, in art rules are for breaking, but you have to understand the rule before you can break it most effectively) Fat Over Lean All mediums are fat, all opaque pigments without medium are lean. You want to paint opaquely first, with little or no medium. In subsequent layers you can move to using more medium because the oil will soak through to the first layer. Also, you don’t want the under layer to dry slower than…
Read More
On 18 Jul, 2015 With
Oil paintings techniques: Vermeer’s Palette Johannes Vermeer was a Dutch painter who specialized in domestic interior scenes of middle-class life. Vermeer was a moderately successful provincial genre painter in his lifetime. He seems never to have been particularly wealthy, leaving his wife and children in debt at his death, perhaps because he produced relatively few paintings. One aspect of his meticulous painting technique was Vermeer’s choice of pigments. He is best known for his frequent use of the very expensive ultramarine (The Milkmaid), and also lead-tin-yellow (A Lady Writing a Letter), madder lake (Christ in the House of Martha and Mary), and vermilion. He also painted with ochres, bone black and azurite. The claim that he utilized indian yellow in Woman Holding…
Read More
On 13 Apr, 2015 With
Venetian Painting Technique The Venetian painting technique was developed from many prior classical painting techniques, and is in effect a culmination of the methods that came before it. The approach to Venetian painting outlined below is a modified version that builds on the Renaissance method, incorporating modern chemicals and a contemporary palette. Venetian painting methods rose to prominence in the 17th century, and were used by painters like Titian, Caravaggio, and Velazquez. The most widespread use of these techniques was witnessed during the Baroque period, and they are ideal for still life painting, portraiture, and compositions that use strong, single-source lighting. The Technique– 1. The first step to creating this type of painting is a basic underdrawing which records the…
Read More
On 22 Jul, 2014 With
Rembrandt was so pleased with his innovation of glazing over dried impasto that he expanded the practice to other textures, devising a method that utilized different whites for impasto and smoother passages. His impasto white was very “lean” and had egg as an ingredient (meaning it must have dried quite quickly), ground glass, and also white lead, which was used as a binder. He generally applied it with increasing thickness in several stages, whereafter it was finished with transparent glazes and wiping, creating the lustre and dimension he is so well-known for. No other technique produces the same brilliance as Rembrandt’s. When he painted Lieutenant Ruytenburch’s uniform in “The Night Watch,” Rembrandt used this method to build up the dimensions…
Read More